Function
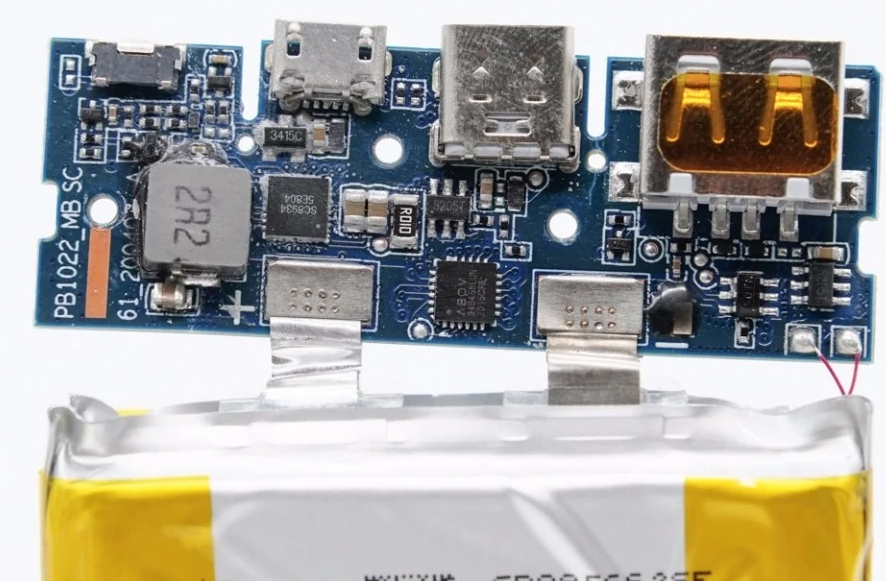
22.5w Power Bank with usb x 2, micro usb x 1, type-c x 1, power key x 1
37Wh 3.7V 10000mAh Rate Capacity: 5500mAh(5V3A)Input: USB-C: 5V3A, 9V2.5A Micro USB: 5V2A, 9V2A Output: 22.5W Max USB-A: 5V2.4A, 9V2.5A, 12V1.85A USB-C: 5V3A, 9V2.5A, 12V1.85A
USB-A1 A2 output support Apple 2.4A, Samsung 5V2A, DCP Protocol, QC2.0/3.0, FCP fast charge Protocol.
USB-C support Apple 2.4A, Samsung 5V2A, DCP, QC2.0, PD3.0, PPS Protocol.
Interface

Size
Power bank with usb-cmini size 90mm x 64mm x 24mm, 199g

Inside
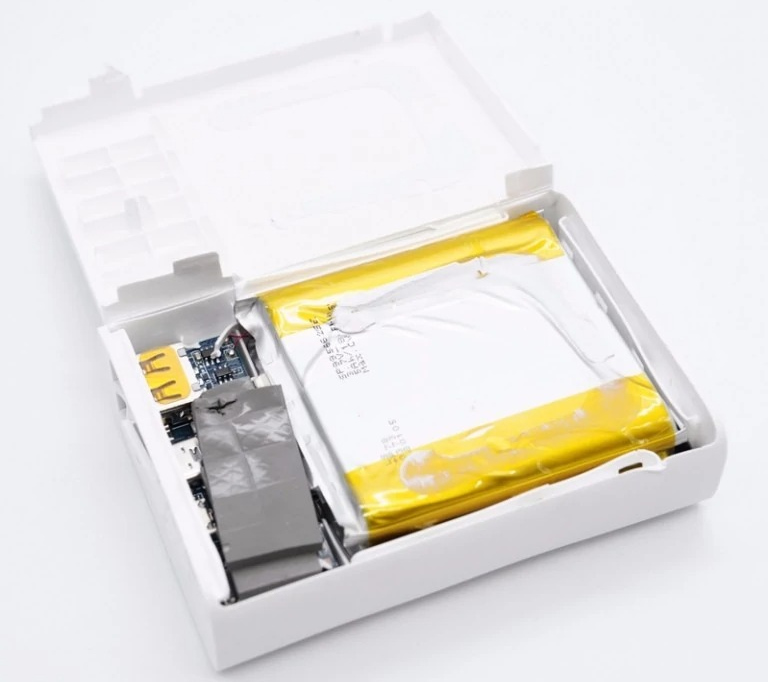
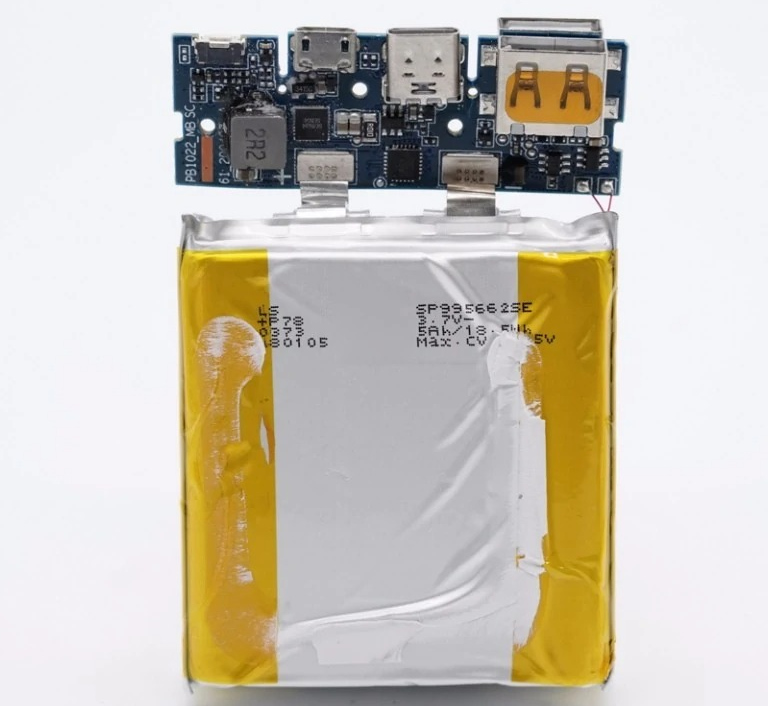


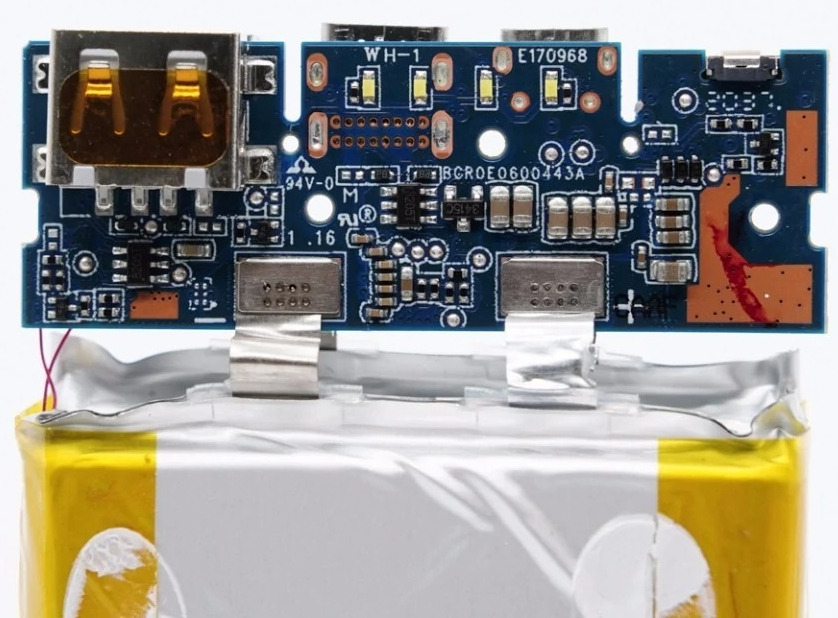
PCBA

CHIPS
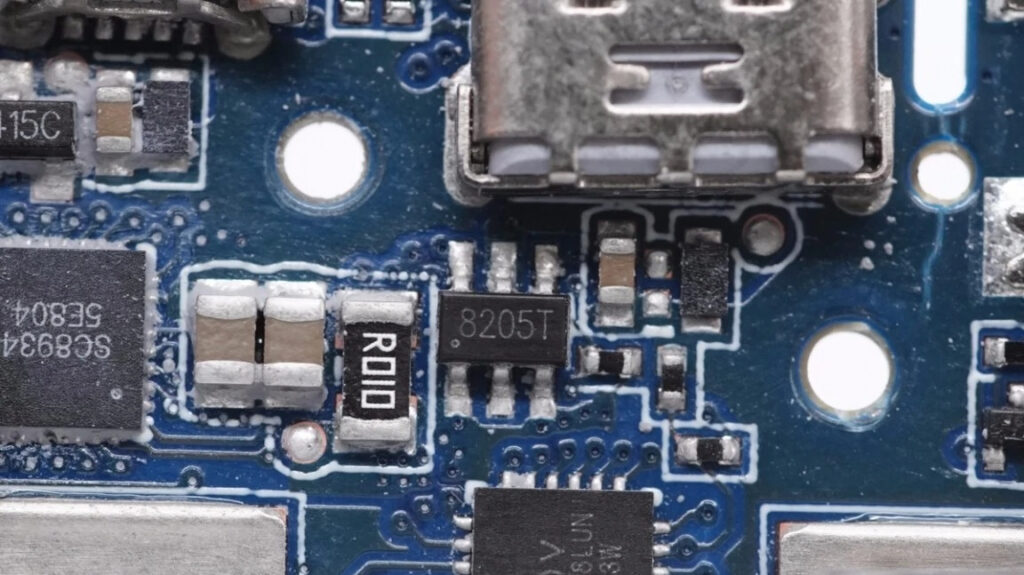
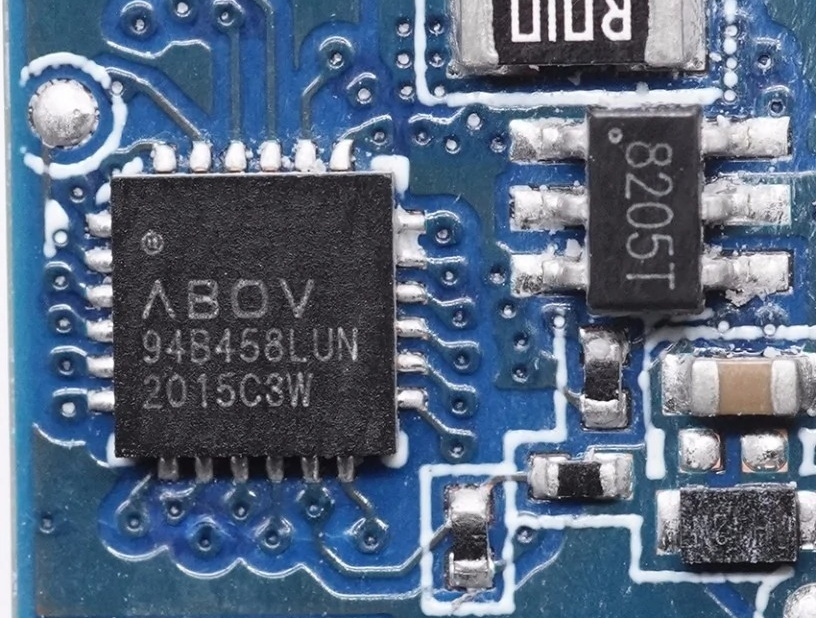
ABOV Semiconductor s Power Solution provides UFC (Universal Fast Charger) MCU and Wireless Charger MCU. UFC MCU is an MCU that supports USB PD3.0 and Legacy high-speed charging. Developers can control UFC (Universal Fast Charge) IP with software to implement the high-speed charging interface required by customers.
Wireless Charger MCU is a single chip with wireless power transmission function.
ABOV A94B458 : USB PD & Legacy USB charging DRP MCU with one USB-C & two USB-A targeted for Power banks
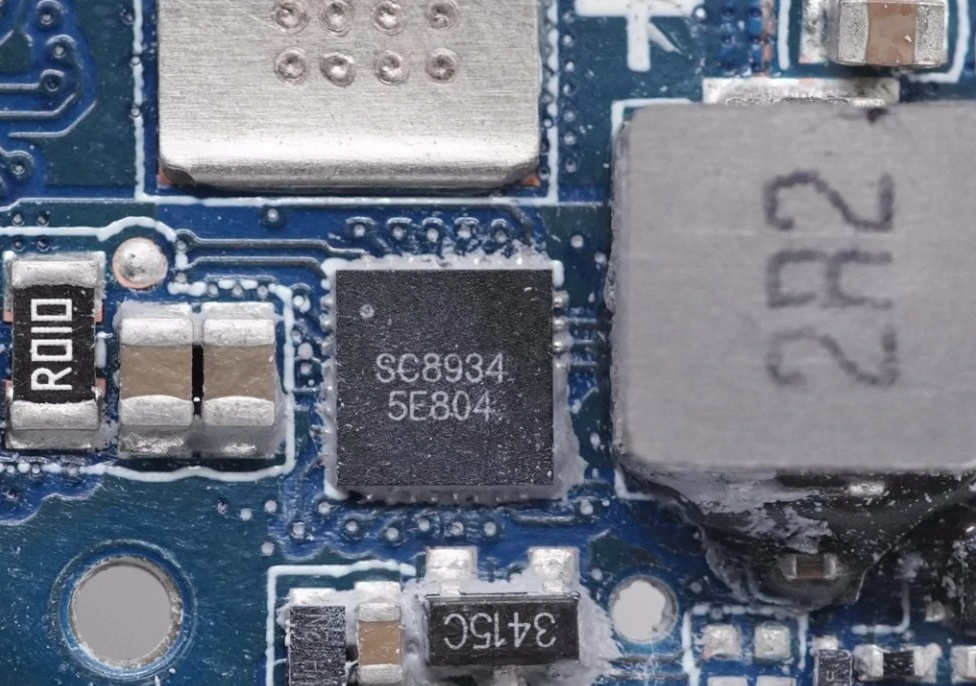

southchip SC8934 High Efficiency, Synchronous, Bi-directional Buck Charger Converter with Integrated MOSFETs and I2C Interface
SC8903 High Efficiency, Synchronous, Bi-Directional Buck-Boost Converter with Four Integrated MOSFET

Difference between QC 1.0 and QC 2.0
- Speed difference: Quite naturally, QC 1.0 isn’t as fast as QC 2.0. According to Qualcomm, QC 2.0 charges devices at least 50 percent faster than QC 1.0. In fact, when standard charging, QC 1.0 and QC 2.0 were subjected to an official 30-minute charge test – traditional charging, QC 1.0 and QC 2.0 charged up identical devices by up to 12 percent, 30 percent, and 60 percent, respectively.
- Voltage variation:
- QC 1.0 supports up to 2A and operates on 5V.
- QC 2.0 works on a multi-voltage charging system offering 5V, 9V and 12V up to 3A. This multistage voltage means when your device battery is really low it charges with 12V, this allows for a really rapid charge, then as the charge gets highest it slowly kicks back the V until you reach normal QC 1.0 voltages and speeds.
What is the difference between PD charging and QC charging?
- Both support fast charging function.
- The PD protocol includes not only Qualcomm’s protocol, but also other fast-charging protocols from major phone companies.
Advantages and disadvantages of PD&QC
- As the industry standard of USB, PD protocol and C-type interface are gradually promoted and accepted by the industry, and are compatible with electronic devices made by more manufacturers. It has the advantages of unified standards and compatibility, and is the future
development trend. - The PD protocol integrates and optimizes two mainstream fast charging modes of high voltage, low current, low voltage and high current, aiming to provide unified, high-efficiency (up to
20VX 5a=100W) fast charging mode. - On PD and c-type interface devices, support forward and reverse insertion, support stronger power transmission (maximum power 100W), faster transmission speed (up to 10Gbps), etc.
- QC fast charging only supports electronic devices using the Qualcomm QC protocol. The orientation of the devices used has certain limitations and cannot be compatible with more charging devices.
- The Qc protocol is a fast charging mode that supports high voltage and low current. It converts the internal capabilities of the mobile phone into low voltage and high current, but it will cause the phone to heat up.
What is the reason that affects the charging speed?
For PD charging and QC charging, there are two different charging methods, that is to say, the comparison is actually the effect of different charging methods on the charging speed under the same charging power!
First of all, it should be pointed out that charging is related to many factors. For example, the selection of devices on the charging path, the wiring impedance on the charging path, the efficiency of the charging chip, the battery capacity and the supported charging methods, etc., and another point is the adjustment of the charging strategy due to the influence of temperature during charging.
Mobile phone PD charging or QC charging which is faster?
The USB PD protocol has been developed to the USB PD3.0 version. The output can be divided into 5V 2A, 12V 1.5A, 12V 3A, 12V5A, 20V 3A, 20V 5A and other different specifications, and the power can reach up to 100W.
For PD charging and QC charging, they have a big difference, that is, the voltage regulation of PD charging is 20mV, and the QC charging is 200mV, which means that the voltage regulation of PD charging will be 10 times finer than that of QC. Considering the safety of the voltage and current of the incoming battery, QC charging will be reserved, and the result is that the QC charging efficiency is relatively low.
Therefore, in comparison, PD charging will be more efficient than QC charging!
Current status and future of QC and PD protocols
The QC protocol is one of the most widely used fast charging protocols by most mobile phone manufacturers (because the market share of Qualcomm’s Snapdragon mobile phone chips is quite large), the PD protocol and the Type-C interface are used as standardized electrical
Industry standards for sub-devices and data transfer are slowly being accepted.
With the release of the USB PD 3.0 charging standard, Qualcomm’s QC 4. was also upgraded and developed into the QC4+ charging standard, compatible with USB PD 3.0, QC 3.0 and QC 2.0.
It can be seen that in addition to Xiaomi, other mobile phone manufacturers compatible with Qualcomm’s latest QC 4+ protocol are small in scale, have a small market share, and support the PD protocol. The brands and models of mobile phones that support the PD protocol include Apple and Huawei.
And Samsung and other first-tier manufacturers, they not only have their own fast charging protocol, but also compatible with PD fast charging mode.
dedicated charging port (DCP)