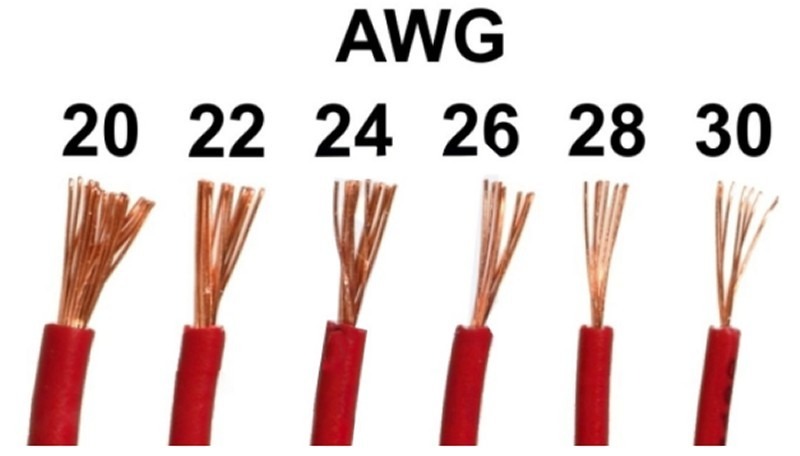
What is American Wire Gauge (AWG)?
American Wire Gauge (AWG Cable) is the standard way to denote wire size in North America. In AWG cable, the larger the number, the smaller the wire diameter and thickness. The largest standard size is 0000 AWG, and 40 AWG Cable is the smallest standard size. It may also be called Brown & Sharpe wire gauge or simply the gauge of the wire.
AWG is for single-strand, solid, round, electrically conductive wire. It was first introduced in 1857 as a standard to replace the various measurements used by different manufacturers. Use of larger numbers denoting smaller wires is similar to Standard Wire Gauge, which is used in Britain. Most other countries use an international metric standard of wire cross-section in square millimeters (mm2) defined in International Electrotechnical Commission 60228.
AWG cable size does not include the size of the insulation protecting a wire.
0000 AWG cable is defined as 0.46 inches in diameter, and 36 AWG cable is defined as 0.005 inches in diameter. All other sizes are derived as logarithmic steps between these two defined sizes. There are 39 gauge steps between these sizes, and the ratio is 1-to-92 in diameter. Therefore, each AWG step is the 39th root of 92, or approximately 1.12293 times the change in diameter.
A smaller gauge (larger size) wire can safely conduct more electricity than a larger gauge (smaller size) wire. Decreasing the AWG cable size of a wire by three will double the cross-sectional area of a wire and double the amount of current it can carry. Changing the AWG cable size by 10 will change the cross-section by tenfold.
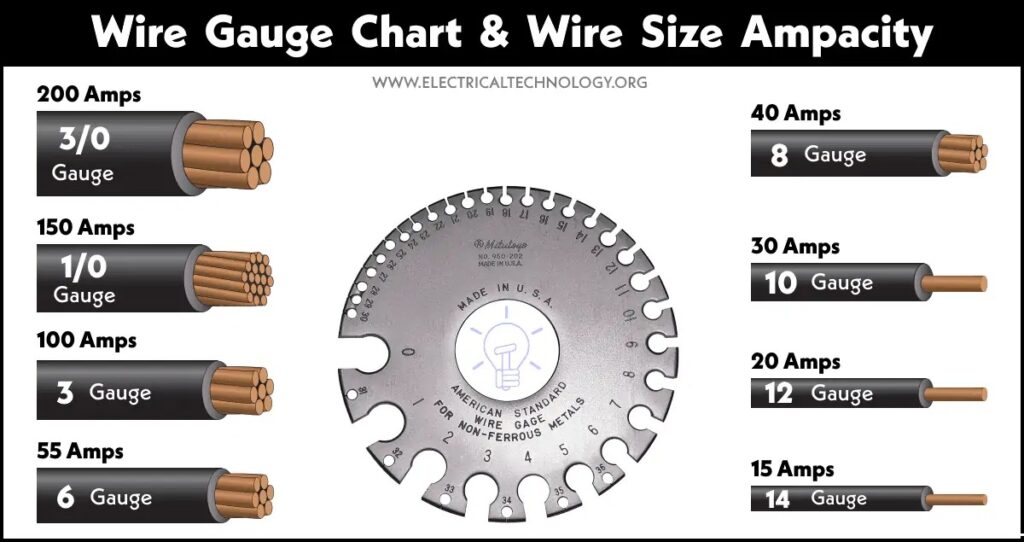
American Conductor Stranding – AWG Table
AWG (Americal Wire Gauge) = Actual Cross Section in mm² and Conductor Resistance
AWG cable is shown below with its exact equivalent value in mm² and diameter (mm).
| AWG Number | Cable Cross Section in mm² | Outer Diameter Ø mm | Conductor Resistance in Ohm/km |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 MCM | 507 | 29,3 | 0,036 |
| 900 | 456 | 27,8 | 0,04 |
| 750 | 380 | 25,4 | 0,048 |
| 600 | 304 | 22,7 | 0,061 |
| 550 | 279 | 21,7 | 0,066 |
| 500 | 253 | 20,7 | 0,07 |
| 450 | 228 | 19,6 | 0,08 |
| 400 | 203 | 18,5 | 0,09 |
| 350 | 177 | 17,3 | 0,10 |
| 300 | 152 | 16,0 | 0,12 |
| 250 | 127 | 14,6 | 0,14 |
| 4/0 | 107,2 | 11,68 | 0,18 |
| 3/0 | 85,0 | 10,40 | 0,23 |
| 2/0 | 67,4 | 9,27 | 0,29 |
| 0 | 53,4 | 8,25 | 0,37 |
| 1 | 42,4 | 7,35 | 0,47 |
| 2 | 33,6 | 6,54 | 0,57 |
| 3 | 26,7 | 5,83 | 0,71 |
| 4 | 21,2 | 5,19 | 0,91 |
| 5 | 16,8 | 4,62 | 1,12 |
| 6 | 13,3 | 4,11 | 1,44 |
| 7 | 10,6 | 3,67 | 1,78 |
| 8 | 8,34 | 3,26 | 2,36 |
| 9 | 6,62 | 2,91 | 2,77 |
| 10 | 5,26 | 2,59 | 3,64 |
| 11 | 4,15 | 2,30 | 4,44 |
| 12 | 3,31 | 2,05 | 5,41 |
| 13 | 2,63 | 1,83 | 7,02 |
| 14 | 2,08 | 1,63 | 8,79 |
| 15 | 1,65 | 1,45 | 11,2 |
| 16 | 1,31 | 1,29 | 14,7 |
| 17 | 1,04 | 1,15 | 17,8 |
| 18 | 0,8230 | 1,0240 | 23,0 |
| 19 | 0,6530 | 0,9120 | 28,3 |
| 20 | 0,5190 | 0,8120 | 34,5 |
| 21 | 0,4120 | 0,7230 | 44,0 |
| 22 | 0,3240 | 0,6440 | 54,8 |
| 23 | 0,2590 | 0,5730 | 70,1 |
| 24 | 0,2050 | 0,5110 | 89,2 |
| 25 | 0,1630 | 0,4550 | 111,0 |
| 26 | 0,1280 | 0,4050 | 146,0 |
| 27 | 0,1020 | 0,3610 | 176,0 |
| 28 | 0,0804 | 0,3210 | 232,0 |
| 29 | 0,0646 | 0,2860 | 282,0 |
| 30 | 0,0503 | 0,2550 | 350,0 |
| 31 | 0,0400 | 0,2270 | 446,0 |
| 32 | 0,0320 | 0,2020 | 578,0 |
| 33 | 0,0252 | 0,1800 | 710,0 |
| 34 | 0,0200 | 0,1600 | 899,0 |
| 35 | 0,0161 | 0,1430 | 1125,0 |
| 36 | 0,0123 | 0,1270 | 1426,0 |
| 37 | 0,0100 | 0,1130 | 1800,0 |
| 38 | 0,00795 | 0,1010 | 2255,0 |
| 39 | 0,00632 | 0,0897 | 2860,0 |
4/0 is also known as 0000; 1 mil = inch = 0,0254 mm
*shown in MCM (circular mills) for bigger cross sections
1 CM = 1 Circ. mil = 0,0005067 mm²
1 MCM = 1000 Circ. mils = 0,5067 mm²
UL/CSA current-carrying capacity for flexible cables
Hook-up wire at ambient temperature up to 30°C
| AWG | Cross Section in mm² | Current-Carrying Capacity in Ampere |
|---|---|---|
| 24 | 0,21 | 3,5 A |
| 22 | 0,33 | 5,0 A |
| 20 | 0,52 | 6,0 A |
| 18 | 0,82 | 9,5 A |
| 16 | 1,31 | 20 A |
| 14 | 2,08 | 24 A |
| 12 | 3,32 | 34 A |
| 10 | 5,26 | 52 A |
| 8 | 8,35 | 75 A |
| 6 | 13,29 | 95 A |
| 4 | 21,14 | 120 A |
| 3 | 26,65 | 154 A |
| 2 | 33,61 | 170 A |
| 1 | 42,38 | 180 A |
Correction-factors at ambient temperature over 30°C
For temperatures over 30°C, multiply the current-carrying capacity in the tables times correction-factor (f) to obtain the allowable current.
| Ambient Temperature °C | Correction-Factor (f) |
|---|---|
| 31-35 | 0,91 |
| 36-40 | 0,82 |
| 41-45 | 0,71 |
| 46-50 | 0,58 |
Multi conductor AWG cable at ambient temperature up to 30°C
| AWG Cable Number | Cross Section in mm² |
Current-Carrying Capacity in Ampere (Number of Cores) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| up to 3 | 4 – 6 | 7 – 24 | 25 – 42 | 43 and above | ||||
| 24 | 0,21 | 2 | 1,6 | 1,4 | 1,2 | 1,0 | ||
| 22 | 0,33 | 3 | 2,4 | 2,1 | 1,8 | 1,5 | ||
| 20 | 0,52 | 5 | 4,0 | 3,5 | 3,0 | 2,5 | ||
| 18 | 0,82 | 7 | 5,6 | 4,9 | 4,2 | 3,5 | ||
| 16 | 1,31 | 10 | 8,0 | 7,0 | 6,0 | 5,0 | ||
| 14 | 2,08 | 15 | 12,0 | 10,5 | 9,0 | 7,5 | ||
| 12 | 3,32 | 20 | 16,0 | 14,0 | 12,0 | 10,0 | ||
| 10 | 5,26 | 30 | 24 | 21 | 18 | 15 | ||
| 8 | 8,35 | 40 | 32 | 28 | 24 | 20 | ||
| 6 | 13,29 | 55 | 44 | 38 | 33 | 27 | ||
| 4 | 21,14 | 70 | 56 | 49 | 42 | 35 | ||
| 3 | 26,65 | 80 | 64 | 56 | 48 | 40 | ||
| 2 | 33,61 | 95 | 76 | 66 | 57 | 47 | ||
| 1 | 42,38 | 110 | 88 | 77 | 66 | 55 | ||
The most common method of referring to conductor sizes uses the cross-sectional area, expressed in mm². The following AWG metric conversion table converts AWG to mm and inches, and also lists the cross sectional area (mm²).
AWG CABLE METRIC CONVERSION CHART (AWG TO MM)
| American Wire Gauge (AWG) | Diameter (in) | Diameter (mm) | Cross sectional area (mm2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0000 (4/0) | 0.460 | 11.7 | 107.0 |
| 000 (3/0) | 0.410 | 10.4 | 85.0 |
| 00 (2/0) | 0.365 | 9.27 | 67.4 |
| 0 (1/0) | 0.325 | 8.25 | 53.5 |
| 1 | 0.289 | 7.35 | 42.4 |
| 2 | 0.258 | 6.54 | 33.6 |
| 3 | 0.229 | 5.83 | 26.7 |
| 4 | 0.204 | 5.19 | 21.1 |
| 5 | 0.182 | 4.62 | 16.8 |
| 6 | 0.162 | 4.11 | 13.3 |
| 7 | 0.144 | 3.67 | 10.6 |
| 8 | 0.129 | 3.26 | 8.36 |
| 9 | 0.114 | 2.91 | 6.63 |
| 10 | 0.102 | 2.59 | 5.26 |
| 11 | 0.0.907 | 2.30 | 4.17 |
| 12 | 0.0808 | 2.05 | 3.31 |
| 13 | 0.0720 | 1.83 | 2.63 |
| 14 | 0.0641 | 1.63 | 2.08 |
| 15 | 0.0571 | 1.45 | 1.65 |
| 16 | 0.0508 | 1.29 | 1.31 |
| 17 | 0.0453 | 1.15 | 1.04 |
| 18 | 0.0403 | 1.02 | 0.82 |
| 19 | 0.0359 | 0.91 | 0.65 |
| 20 | 0.0320 | 0.81 | 0.52 |
| 21 | 0.0285 | 0.72 | 0.41 |
| 22 | 0.0254 | 0.65 | 0.33 |
| 23 | 0.0226 | 0.57 | 0.26 |
| 24 | 0.0201 | 0.51 | 0.20 |
| 25 | 0.0179 | 0.45 | 0.16 |
| 26 | 0.0159 | 0.40 | 0.13 |